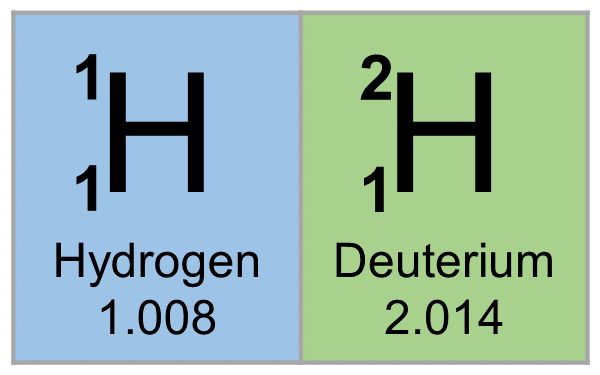
Atomic Number of Hydrogen is 1.
- Hydrogen - Element Information, Properties And Uses ...
- What Is The Atomic Number For Hydrogen? + Example
Quantum Numbers, Hydrogen Atom In the solution to the Schrodinger equation for the hydrogen atom, three quantum numbers arise from the space geometry of the solution and a fourth arises from electron spin.
Hydrogen - Element Information, Properties And Uses ...
Chemical symbol for Hydrogen is H. Number of protons in Hydrogen is 1. Atomic weight of Hydrogen is 1.008 u or g/mol. Melting point of Hydrogen is -259,1 °C and its the boiling point is -252,9 °C.
» Boiling Point» Melting Point» Abundant» State at STP» Discovery Year- Hydrogen is a chemical element with symbol H and atomic number 1. Classified as a nonmetal, Hydrogen is a gas at room temperature.
- Quantum Numbers, Hydrogen Atom In the solution to the Schrodinger equation for the hydrogen atom, three quantum numbers arise from the space geometry of the solution and a fourth arises from electron spin.
About Hydrogen
Known as the most abundant and the lightest chemical element in our Universe, hydrogen is a type of gas without color and smell, which also has the lowest density of all gases. It is believed to be the first atom produced in our Universe after the Big Bang, and all other elements were further produced from hydrogen as a result of nuclear fusion. The name of the gas is formed from two Greek words, meaning water and forming, so this is the element which creates water. Since hydrogen is a part of water molecule, it is an absolutely essential chemical element for life, which can be found in all living bodies on our planet. It is extensively used in a large variety of industrial branches, from chemical industry (producing fertilizers, etc) to electronic (substance producing) and food industry, etc. One more very important point is: hydrogen is now seen as a source of clean eco-friendly fuel of the future, which will help the humanity to solve the problem of pollution and being gas/oil dependent.
Uses of Hydrogen
Hydrogen is mostly used in the petroleum and chemical industries. The most important use of hydrogen in the world is in ammonia manufacture for the fertilizer market. The other significant use of this chemical element is in fossil fuel processing. Today, liquid hydrogen is used as a primary fuel of the American space program by The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). Hydrogen is also used in various industrial fields such as metalworking and as a coolant in generators in power stations.
Compounds with Hydrogen

- H2O = Water (2 hydrogen, 1 oxygen)
- CH4 = Methane (1 carbon, 4 hydrogen)
- NH3 = Ammonia (1 nitrogen, 3 hydrogen)
- C6H12O6 = Glucose
- C9H8O4 = Aspirin
- NaHCO3 = Baking Soda
- C2H6O = Alcohol
- C12H22O11 = Sugar
- CH3COCH3 = Acetone
- C3H8 = Propane
- C2H4O2 = Acetic Acid
- HCI = Hydrochloric Acid
- C6H8O6 = Ascorbic Acid
- C3H6O3 = Lactic Acid
- H2S = Hydrogen Sulfide
- C2H4O2 = Vinegar
- C2H6O = Ethanol
- C4H10 = Butane
- C12H22O11 = Sucrose
- H2O2 = Hydrogen Peroxide
- NaOH = Sodium Hydroxide
- C6H6 = Benzene
- C10H16O = Camphor
- H2S = Hydrogen Sulfide
- CH3OH = Methanol
Properties of Hydrogen Element
| Atomic Number (Z) | 1 |
|---|---|
| Atomic Symbol | H |
| Group | 1 |
| Period | 1 |
| Atomic Weight | 1.008 u |
| Density | 0.00008988 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point (K) | 14.01 K |
| Melting Point (℃) | -259,1 °C |
| Boiling Point (K) | 20.28 K |
| Boiling Point (℃) | -252,9 °C |
| Heat Capacity | 14.304 J/g · K |
| Abundance | 1400 mg/kg |
| State at STP | Gas |
| Occurrence | Primordial |
| Description | Non-metal |
| Electronegativity (Pauling) χ | 2.2 |
| Ionization Energy (eV) | 13.59844 |
| Atomic Radius | 25pm |
| Covalent Radius | 38pm |
| Van der Waals Radius | 120 |
| Valence Electrons | 1 |
| Year of Discovery | 1766 |
| Discoverer | Cavendish |
What is the Boiling Point of Hydrogen?
Hydrogen boiling point is -252,9 °C. Boiling point of Hydrogen in Kelvin is 20.28 K.
What is the Melting Point of Hydrogen?
Hydrogen melting point is -259,1 °C. Melting point of Hydrogen in Kelvin is 14.01 K.
How Abundant is Hydrogen?
Abundant value of Hydrogen is 1400 mg/kg.
What is the State of Hydrogen at Standard Temperature and Pressure (STP)?
What Is The Atomic Number For Hydrogen? + Example

State of Hydrogen is Gas at standard temperature and pressure at 0℃ and one atmosphere pressure.
When was Hydrogen Discovered?
Hydrogen was discovered in 1766.
We elaborate the uses of Hydrogen and atomic properties with characteristics. Hydrogen is a colorless-looking chemical element with atomic number 1. Its symbol is H and it belongs to the group of nonmetals and its usual state in nature is gaseous. Hydrogen is located at position 1 on the periodic table.
You Can Visit Our Managed: Periodic Table Main Page
On this post you can discover the chemical properties of hydrogen and information about hydrogen and other elements on the periodic table such as lithium, helium, beryllium or sodium. You will also learn what hydrogen is for and learn about its uses through its properties associated with hydrogen such as its atomic number or the usual state in which hydrogen can be found.

You will see qualities of hydrogen such as its melting and boiling point, its magnetic properties or what its chemical symbol is. In addition, here you will find information about its atomic properties such as the distribution of electrons in hydrogen atoms and other properties.
For some elements, some of this information is unknown. In these cases we show the properties attributed to them.
Properties of hydrogen
One of the properties of non-metal elements like hydrogen is for example that non-metal elements are poor conductors of heat and electricity. Hydrogen, like the other nonmetals, has no luster. Due to their brittleness, nonmetals such as hydrogen cannot be flattened to form sheets or stretched to become threads.
The state of hydrogen in its natural form is gaseous. Hydrogen is a colorless-looking chemical element and belongs to the group of nonmetals. The atomic number of hydrogen is 1. The chemical symbol for hydrogen is H. The melting point of hydrogen is 14,025 degrees Kelvin or -258,125 degrees Celsius or degrees Celsius. The boiling point of hydrogen is 20,268 degrees Kelvin or -251,882 degrees Celsius or degrees Celsius.
Uses of hydrogen
Hydrogen is a chemical element with an atomic number 1. It is usually placed in the upper left corner of the periodic table. Many people ask me ‘what are some of the common uses of hydrogen? If you’ve ever wondered what hydrogen is for , here is a list of its possible uses:
- It is used to process fossil fuels.
- It is used to produce ammonia used in common household cleaning products.
- Hydrogen is used as a hydrogenating agent to produce methanol and convert unhealthy unsaturated fats and oils to saturated fats and oils.
- The triple point of hydrogen (the temperature at which the 3 states, solid, liquid, and gas are in equilibrium) can be used to calibrate some thermometers.
- Tritium, a radioactive isotope of hydrogen, is produced in nuclear reactions. It can be used to make hydrogen bombs and acts as a radiation source in light paints. In the biological sciences, tritium is sometimes used as an isotopic marker.
- Hydrogen (either used alone or combined with nitrogen) is used in many manufacturing plants to determine if there are leaks. It is also used to detect leaks in food packaging .
- Hydrogen is used as a rotor coolant in electric generators.
- Hydrogen in the gaseous state is used as a shielding gas in atomic hydrogen welding.
- It is also used in the production of hydrochloric acid, widely used in the chemical industries.
- Hydrogen gas is used to reduce many metallic minerals.
- It can be used to create water .
Atomic properties of hydrogen
The electronic configuration of hydrogen is 1s1. The electronic configuration of the elements, determines the form in which the electrons are structured in the atoms of an element. The average radius of hydrogen is 25 pm, its atomic radius or Bohr radius is 53 pm, its covalent radius is 37 pm, and its Van der Waals radius is 120 pm. Hydrogen has a single electron located in its first shell.
You Can Visit Our Managed: Periodic Table Main Page

Hydrogen characteristics
Below you can see a table where the main characteristics of hydrogen are shown.
| Hydrogen | ||
|---|---|---|
| Chemical symbol | H | |
| Atomic number | 1 | |
| Group | 1 | |
| Period | 1 | |
| Appearance | colorless | |
| Block | s | |
| Density | 0.0899 kg / m3 | |
| Average radius | 25 pm | |
| Atomic radio | 53 | |
| Covalent radius | 37 pm | |
| Van der Waals radio | 120 pm | |
| Electronic configuration | 1s1 | |
| Electrons per layer | one | |
| Oxidation states | eleven | |
| Oxide | amphoteric | |
| Crystal structure | hexagonal | |
| State | gaseous | |
| Melting point | 14,025 K | |
| Boiling point | 20,268 K | |
| Flash point | 255 K | |
| Heat of fusion | 0.05868 kJ / mol | |
| Vapor pressure | 209 Pa to 23 K | |
| Critical temperature | 23.97 K | |
| Critical pressure | 1,293106 Pa | |
| Molar volume | 22.42 × 10-3m3 / mol | |
| Electronegativity | 2.2 | |
| Specific heat | 1,4304104J / (Kkg) | |
| Electric conductivity | – Ye | |
| Thermal conductivity | 0.1815 W / (Km) | |
You Can Visit Our Managed: Periodic Table Main Page
